In this blog, I will explore the role and responsibilities of an SDET (Software Development Engineer in Test), providing insights into different types of testing and popular test automation frameworks. While I will introduce various testing frameworks, the main focus will be on Robot Framework and pytest, highlighting their features, use cases, and advantages in modern test automation.
Daily work
Bug Reporting
- Bug reporting system eg.Jira (ASSIGN, VIEW, TRIAGE, REPORT, CLOSE)
- Ticket include key as title, description, software version, steps to reproduce, expected result, actual result, screenshot, logs, prioriy/severity, status.
Test Planning + Execution
- Sheet include scenarios, expected, latest result, automate(bool); include happy path, sad path, and edge case
Build/Leverage Tool
- Use bash script/python3 to build hands-on tool
- Contribute to test frameworks(build as module instead of script)
- Use third-party to monitor acitivity such as Grafana to visualize networking data
- Build scalable application for large volume of data processing and data visualization, considering efficient data structure and algorithm to search/query output’s combination
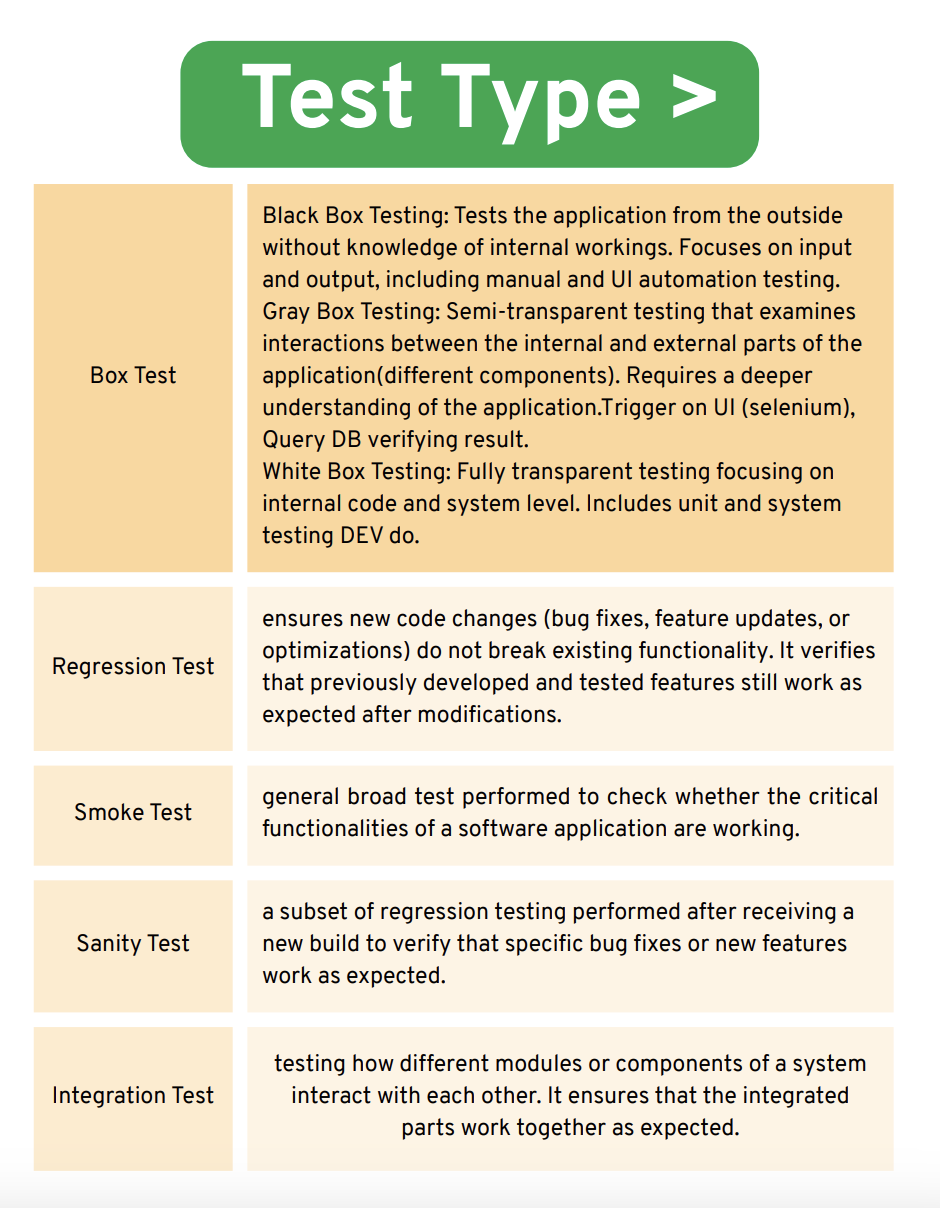
Test Type
Test Framework
| Framework | Language(s) | Type | Best for | Ease of Use | Parallel Execution | Integration Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pytest | Python | Unit, API, UI | Unit tests, API tests | Easy | Yes (pytest-xdist) | CI/CD, Selenium |
| Cypress | JavaScript | UI, E2E | Web UI automation | Easy | Yes (built-in) | CI/CD, API Testing |
| Robot | Multi | UI, API, E2E | Keyword-driven testing | Moderate | Yes | Selenium, Appium |
| Selenium | Multi | UI, E2E | Web UI automation | Moderate | No (requires setup) | CI/CD, Appium |
| JUnit | Java | Unit | Java Unit Testing | Easy | Yes (JUnit 5) | CI/CD, Spring |
| Mocha | JavaScript | Unit, API | JS Unit and API Testing | Easy | Yes (Mocha-parallel) | CI/CD, Browser |
| Playwright | JavaScript | UI, E2E | Fast UI testing | Moderate | Yes (built-in) | CI/CD, API Testing |
| TestCafe | JavaScript | UI, E2E | Cross-browser UI Testing | Easy | Yes (built-in) | CI/CD |
| JMeter | Java | Performance | Load and Stress Testing | Hard | Yes | CI/CD, API Testing |
| Locust | Python | Performance | Load Testing (Python) | Moderate | Yes | API, Web Apps |
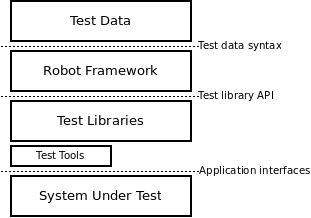
Robot Overview
Robot Framework uses human-readable keywords to write test cases (instead of code-heavy scripts). It acts as a Python wrapper with libraries, providing:
✔ Clear pass/fail reports
✔ Automatic screenshots on failure (if configured)
✔ Detailed logs for every test case
test.robot
1 | *** Settings *** |
In common.robot
1 | *** Settings *** |
In Robot_framework.py
1 | import subprocess |
Run test:
1 | $ robot test.robot |
Pytest Overview
Key Features of Pytest
✔ Assertions – Detailed failure reports with assert statements.
✔ Fixtures – Reusable setup/teardown functions (more below).
✔ Parametrization – Run the same test with different inputs.
✔ Plugins – Extensible with a large ecosystem (e.g., pytest-cov for coverage).
Pytest Fixture Usage
In pytest, fixtures are functions that are executed before and after each test. We can use fixtures to prepare data and make it available to our test cases.
In api.py
1 | class Calculator: |
In conftest.py
1 | import pytest |
In test.py
1 | def test_basic_addition(calc): |
Run test:
1 | $ pytest test.py |
Where Run Test
- Choice: In local, run isolated Dockers, write entry file to start Docker, begin setup, testing and teardown setup.
- Choice: Integrate with CICD(e.g, Jenkins), write jenkinsfile and start docker inside of Jenkin runner. If tests pass, teardown setup and docker container; otherwise, stuck there to let QA to troubleshoot failure point.
