While working on a Grafana dashboard that connects to SQL, I used SQL queries and implemented test automation to simulate user input, modify/lookup the database and verify expected results. This blog post documents my knowledge of SQL. I will use https://www.sql-practice.com/ patient system as my part of query data, you can try it by yourself.
SELECT
Aggregate functions
CONCAT
Exampe: Show first name and last name concatinated into one column to show their full name
1 | SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) AS full_name FROM patients; |
COUNT
Example: Show how many patients have a birth_date with 2010 as the birth year
1 | SELECT count(distinct patient_id) AS total_patients FROM patients WHERE birth_date like '2010%'; |
MAX/MIN
Example: Show the first_name, last_name, and height of the patient with the greatest height
1 | SELECT first_name, last_name, MAX(height) FROM patients; |
SUM
Example: count total number of male and female
1 | SELECT SUM(gender='M') AS male_count, SUM(gender='F') AS female_count FROM patients; |
FROM
INNER JOIN
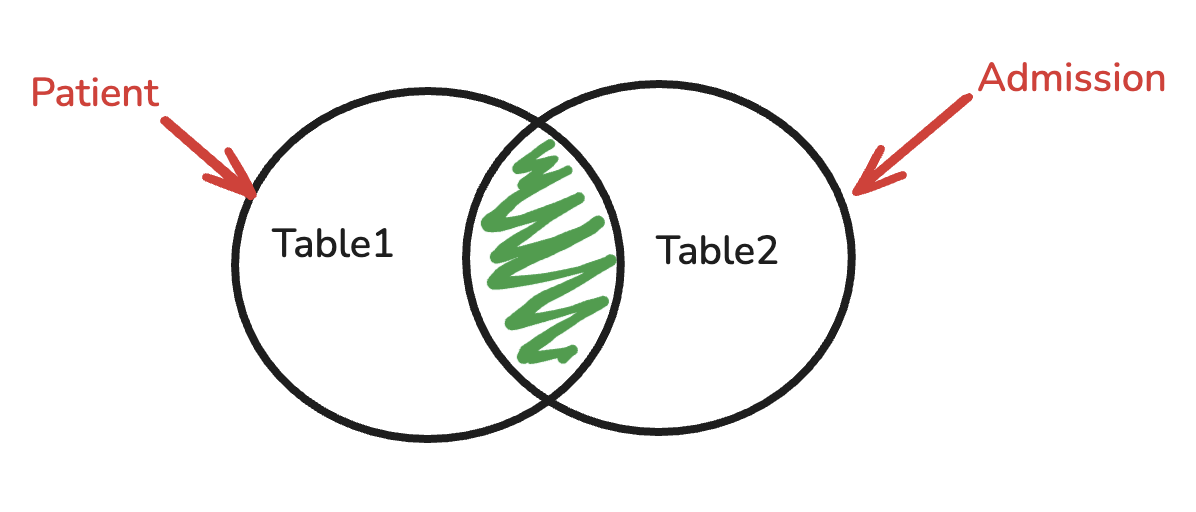
Check common information from two tables
1 | SELECT DISTINCT p.patient_id, p.first_name, p.last_name FROM patients p JOIN admissions a |
LEFT/RIGHT JOIN
Left Join will display all data, right table will know result based on ON query, if not found return NULL.
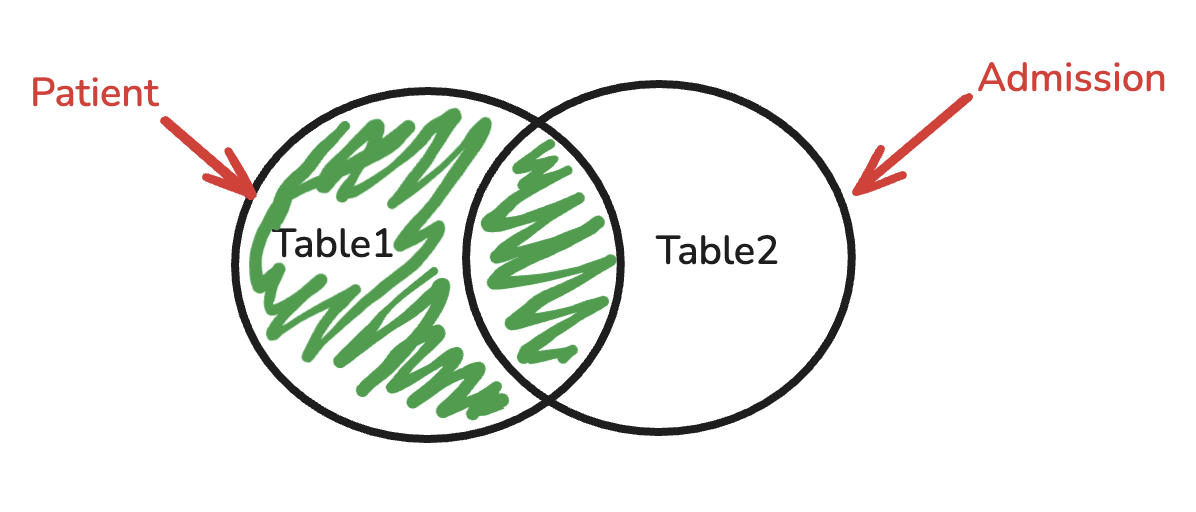
| Join Type | Priority Table | Includes Non-Matches From | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEFT JOIN | Left table | Left table | Find all patients, with admissions if they exist |
| RIGHT JOIN | Right table | Right table | Find all admissions, with patient data if it exists |
Example: table ordered by travelled_distance in descending order, if two or more users traveled the same distance, order them by their name in ascending orderIFNULL(func, 0) set 0 if value is null.
1 | SELECT u.name, IFNULL(SUM(r.distance),0) AS travelled_distance |
UNION ALL
UNION ALL combines both result set(keeps duplicates if any exist)
Example: Show first name, last name and role of every person that is either patient or doctor. The roles are either “Patient” or “Doctor”
1 | SELECT first_name, last_name, 'Patient' AS role FROM patients |
WHERE Clause
Operator -> = > >= < <= != AND OR NOT
1 | SELECT first_name,last_name,birth_date FROM patients WHERE height > 160 AND weight > 70; |
Check NULL -> IS NULL
Example: Show first name and last name of patients who does not have allergies. (null)
1 | SELECT first_name, last_name FROM patients WHERE allergies IS NULL; |
Example: Update the patients table for the allergies column. If the patient’s allergies is null then replace it with ‘NKA’
1 | UPDATE patients SET allergies = 'NKA' WHERE allergies is NULL; |
Fuzzy query -> LIKE %
Example: Show first name of patients that start with the letter ‘C’
1 | SELECT first_name FROM patients WHERE first_name LIKE 'C%'; |
Example: Show patient_id and first_name from patients where their first_name start and ends with ‘s’ and is at least 6 characters long
1 | SELECT DISTINCT patient_id, first_name FROM patients WHERE first_name LIKE 's%s' AND LENGTH(first_name) >=6; |
Range query
BETWEEN … AND … (between two values)
Example: Show first name and last name of patients that weight within the range of 100 to 120 (inclusive)
1 | SELECT first_name, last_name FROM patients WHERE weight BETWEEN 100 AND 120; |
In() (check if in this values)
Example: Show all columns for patients who have one of the following patient_ids: 1,45,534,879,1000
1 | SELECT * FROM patients WHERE patient_id in (1,45,534,879,1000); |
GROUP BY Clause
Example: Show the city and the total number of patients in the city.Order from most to least patients and then by city name ascending
1 | SELECT city, COUNT(distinct patient_id) AS num_patients FROM patients GROUP BY city ORDER BY num_patients DESC, city ASC; |
Example: Show all allergies ordered by popularity. Remove NULL values from query
1 | SELECT allergies, COUNT(*) AS total_diagnosis FROM patients WHERE allergies IS NOT NULL |
HAVING Clause
We knows WHERE filters individual row before aggregation, HAVING filters groups after aggregation. Always use HAVING and GROUP BY when filtering by aggregated result.
Example: Show unique first names from the patients table which only occurs once in the list.
1 | SELECT first_name FROM patients GROUP BY first_name HAVING count(first_name)=1 ORDER BY first_name; |
Example: Show patient_id, diagnosis from admissions. Find patients admitted multiple times for the same diagnosis
1 | SELECT patient_id, diagnosis FROM admissions GROUP BY patient_id, diagnosis HAVING COUNT(*)>1; |
ORDER BY Clause
ORDER BY <columnNo/ColumnName>
Example: Show unique birth years from patients and order them by ascending
1 | SELECT distinct YEAR(birth_date) FROM patients order by birth_date; |
